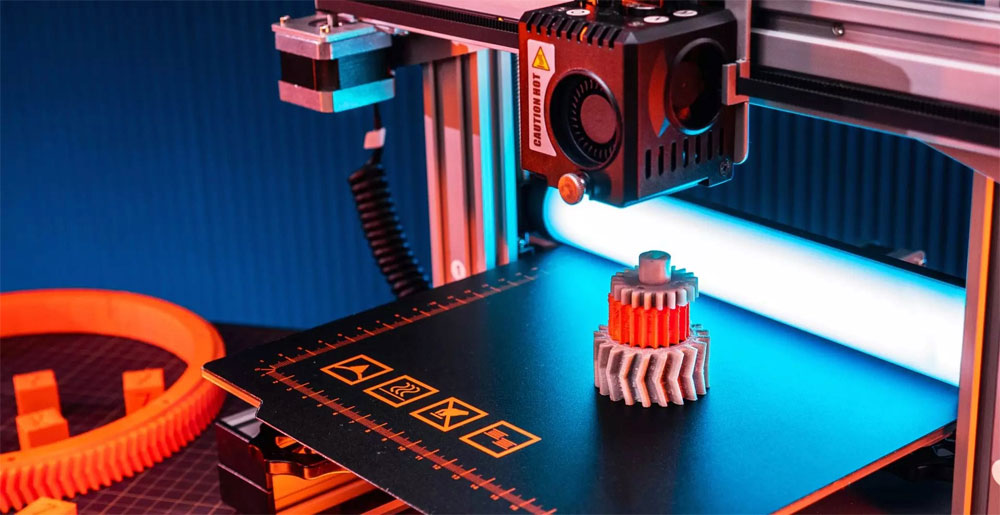
Layered Construction: Additive manufacturing begins with a digital 3D replica of the desired object. This method continuously adds thin cross-sections or layers to build a 3D result.
Diverse Materials: Depending on technology and printers, a selection of materials can be used within additive manufacturing including plastics, metals and ceramics.
Rapid Prototyping: Designers and engineers use additive manufacturing for rapid prototyping, enabling them to quickly create prototypes before committing to large-scale production. Find out more about rapid prototyping here.
Reduced Waste: Traditional manufacturing often generates significant material waste, however additive manufacturing is more material-efficient since it only uses the material necessary to build the object.
Customisation: This manufacturing solution is used in various industries, including aerospace, healthcare, automotive, and consumer goods, to create personalised products and components. This includes the creation of one-off goods.
Complex Assemblies: Some additive manufacturing techniques can produce complete assemblies of interconnected parts in a single printing process. This can reduce the need for assembly and improve the structural integrity of the final product.
Digital Control: This process is digitally controlled, from the initial 3D modelling to the printing itself. Meaning man-made input is less frequent. This allows for precise control and repeatability, allowing manufacturers to edit and change things remotely, without affecting the production line.